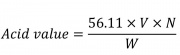Difference between revisions of "Acid Value"
| (19 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | Acidity is frequently expressed as the Acid Value, which is the number of mg of potassium hydroxide required to neutralize the free acids in 1.0 g of the substance. | + | Acidity is frequently expressed as the Acid Value, which is the number of mg of potassium hydroxide required to neutralize the free acids in 1.0 g of the substance<ref>Warth, A. H.; The Chemistry and Technology of Waxes. Reinhold Publishing Corporation. Second Edition, p. 586</ref>. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | The | + | =Methods= |
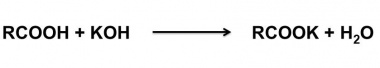
| + | The acid value of a wax is determined by dissolving a known amount of the wax in alcohol and titrating the solution against standard alkali solution. | ||
| − | + | [[File:Acid_reaction.jpg|380x380px|centro|]] | |
| − | + | ==USP 401== | |
| + | The acidity of fats and fixed oils in USP may be expressed as the number of mL of 0.1 N alkali required to neutralize the free acids in 10.0 g of substance<ref>Pharmacopedia/National Formulary. US., Vol. 1, 2009, p. 150</ref>. | ||
| − | + | Weigh 3 g of sample and place it in a clean 250 mL Erlenmeyer flask. Place 50 mL of solvent (isopropyl alcohol-toluene 5:4) connect the flask with a suitable condenser and warm slowly, with frequent shaking, until the sample dissolves. Remove the flask from the condenser and add 1 mL of phenolphthalein in isopropyl alcohol. | |
| + | Shake vigorously while titrating with 0.1 N potassium hydroxide. Register the volume of potassium hydroxide consumed.Calculate Acid value by the formula: | ||
| + | [[File:Diapositiva1.JPG|180x180px|centro|]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Which: | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | 56.11: is the molecular weight of potassium hydroxide | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | V: is the volume in mL | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | N: is the normality of the potassium hydroxide solution | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | W: is the weight, in g, of the sample taken | |
| − | + | ||
| − | |||
==Referencia== | ==Referencia== | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | <references /> | |
Latest revision as of 15:12, 14 June 2018
Acidity is frequently expressed as the Acid Value, which is the number of mg of potassium hydroxide required to neutralize the free acids in 1.0 g of the substance[1].
Methods
The acid value of a wax is determined by dissolving a known amount of the wax in alcohol and titrating the solution against standard alkali solution.
USP 401
The acidity of fats and fixed oils in USP may be expressed as the number of mL of 0.1 N alkali required to neutralize the free acids in 10.0 g of substance[2].
Weigh 3 g of sample and place it in a clean 250 mL Erlenmeyer flask. Place 50 mL of solvent (isopropyl alcohol-toluene 5:4) connect the flask with a suitable condenser and warm slowly, with frequent shaking, until the sample dissolves. Remove the flask from the condenser and add 1 mL of phenolphthalein in isopropyl alcohol. Shake vigorously while titrating with 0.1 N potassium hydroxide. Register the volume of potassium hydroxide consumed.Calculate Acid value by the formula:
Which:
56.11: is the molecular weight of potassium hydroxide
V: is the volume in mL
N: is the normality of the potassium hydroxide solution
W: is the weight, in g, of the sample taken